Cloud native EDA tools & pre-optimized hardware platforms
Photonic Solutions Enewsletter
Impact of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS) on Fiber’s Effective Loss
Spontaneous or stimulated scattering of light in optical fiber can be caused by Rayleigh, Raman and Brillouin scattering. These effects are present irrespective of the amount of optical power, although higher intensity can cause stronger scattering effects. Out of these three types of scattering, Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS) is often a dominant type of fiber nonlinearity. The SBS is an acousto-optic interaction that restricts the amount of power that can be transmitted in fibers1.
The parameters to model the SBS effect in OptSim can be accessed from the nonlinear fiber’s parameter window:
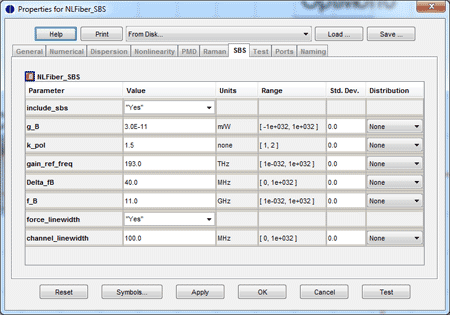
The layout shown below demonstrates the effect of SBS on a fiber’s transmission performance, namely signal loss. The launch power of an SMF-28 fiber’s input signal is increased until SBS becomes important and begins depleting the input signal. In the top branch of the topology, SBS is included in the model. In the bottom branch, it is not. All other fiber parameters are identical, including the length of 20 km. This setup allows us to determine at what fiber launch power SBS begins to have an effect.
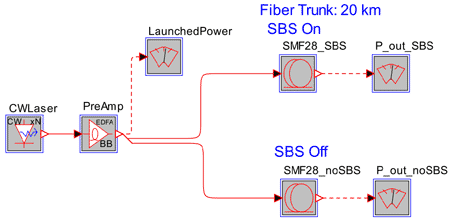
The results are shown in the plots below. The Y-axis plots the fiber’s output power, while the X-axis shows the power launched into the fiber.
By comparing the results, we see that at a launch power of approximately 14 dBm, the output of the fiber begins to be depleted (left) relative to that of the non-SBS fiber (right). Beyond 14 dBm, the output is clearly reduced by the SBS effect.
We hope you found this information helpful. If you have any questions, please contact us at rsoft_support@synopsys.com
1G. P. Agrawal, Nonlinear Fiber Optics, 2nd Edition (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1995).
Important Changes to RSoft Products Platform Support in 2014
In April 2014, Microsoft stopped supporting Windows XP. In addition, usage of several other platforms currently supported by the RSoft products, such as Windows Vista, has drastically decreased. Therefore, RSoft products versioned 2013.12 are the last versions to officially support the following operating systems:
- Windows XP
- Windows Vista
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 4
- All 32-bit Windows and Linux versions
Please note that service releases for RSoft products versioned 2013.12 will also support Windows XP, Windows Vista, RHEL 4, and 32-bit versions of Windows and Linux.
Beginning in mid-2014, RSoft products beyond version 2013.12 will only officially support the following platforms:
- 64-bit Windows 7
- 64-bit Linux
We encourage you to migrate to 64-bit Windows or Linux computers, since official support for 32-bit versions of these operating systems will end in mid-2014. If you have any questions, please contact rsoft_support@synopsys.com.






